38. Electroreductive Borylation of Chloroalkanes and Polyvinyl Chloride Plastics. Onuigbo, O.I.; Zackasee, J.L.; Srivardhan, V.; Spejcher, J.A.; Sevov, C.S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025.

37. Nickel-mediated aerobic Csp2–nucleophile coupling. Das, D.; Dinh, L.P.; Smith, R.E.; Kalyani, D.; Sevov, C.S. Trends Chem. 2025. (mechanism of the month).

36. Cyclometallated Co(III) Complexes with Lowest-Energy Charge Transfer Excited States Accessible with Visible Light. Burton, S.T.; Lee, G.; Moore, C.E.; Sevov, C.S.; Turro, C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2025, 147, 13315.

35. Nickel-mediated aerobic C(sp2)–nucleophile coupling reactions for late-stage diversification of aryl electrophiles. Das, D.; Dinh, L.P.; Smith, R.E.; Kalyani, D.; Sevov, C.S. Nat. Synth. 2025

34. Aminoborate-Catalyzed Reductive Counterreactions for Oxidative Electrosynthetic Transformations. Smith, R.E., Dinh, L.P., Sevov, C.S. J. Org. Chem. 2024, 89, 18550

33. Electrocatalytic Grafting of Polyvinyl Chloride Plastics. Zackasee, J. L. S.; Srivardhan, V.; Truesdell, B. L.; Vrana, E. J.; Sevov, C. S. Chem 2024.

• Highlighted in The Ohio State News.
• Article highlight in Chem by Liu & Duan.
32. Reductive Alkyl-Alkyl Coupling from Isolable Nickel-Alkyl Complexes. Al Zubaydi, S.; Waske, S.; Akyildiz, V.; Starbuck, H. F.; Majumder, M.; Moore, C. E.; Kalyani, D.; Sevov, C. S. Nature 2024.

• Writeup in Nature News & Views from the Diao group.
• Article in Drug Discovery News.
• Highlighted in The Ohio State News.
31. Persistent Organonickel Complexes as General Platforms for Csp2–Csp3 Coupling Reactions. Dinh, L. P.; Starbuck, H. F.; Hamby, T. B.; LaLama, M. J.; He, C. Q.; Kalyani, D.; Sevov, C. S. Nat. Chem. 2024.

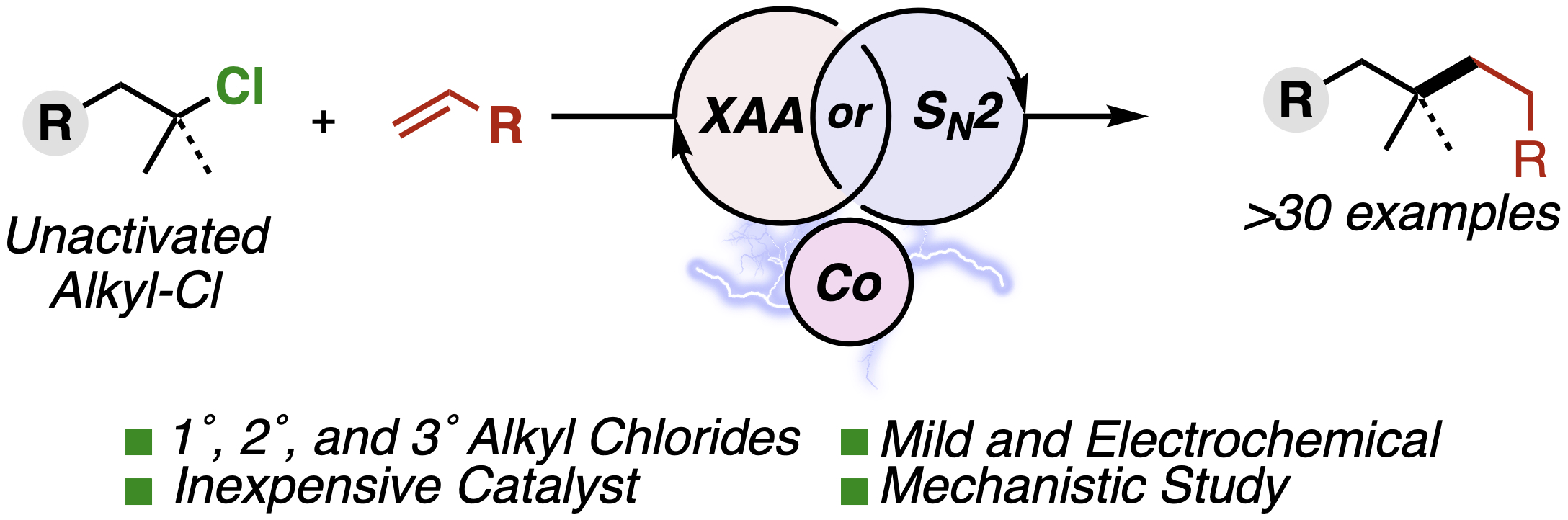
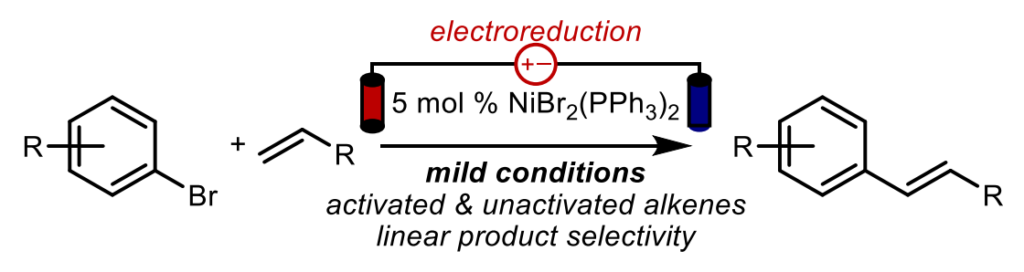
30. Cobalt‐Catalyzed Electroreductive Alkylation of Unactivated Alkyl Chlorides with Conjugated Olefins. Al Zubaydi, S.; Onuigbo, I. O.; Truesdell, B. L.; Sevov, C. S.; Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2023, e202313830.
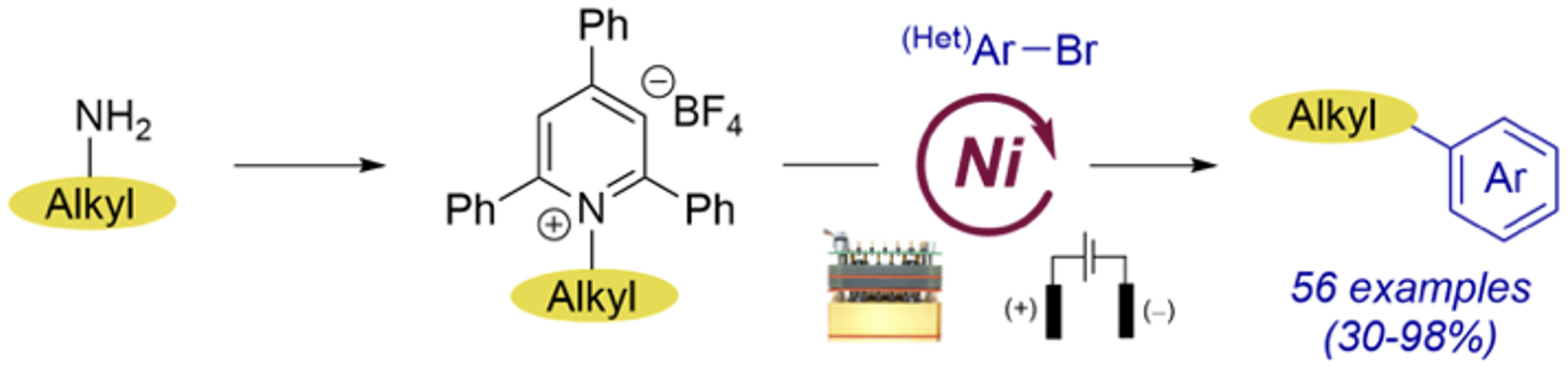
29. Nickel-Catalyzed Electroreductive Coupling of Alkylpyridinium Salts and Aryl Halides. Fu, J.; Lundy, W.; Chowdhury, R.; Twitty, C.J.; Dinh, L.; Sampson, J.; Lam, Y.; Sevov, C.S.; Watson, M.; Kalyani, D. ACS Catal. 2023, 13, 9336.
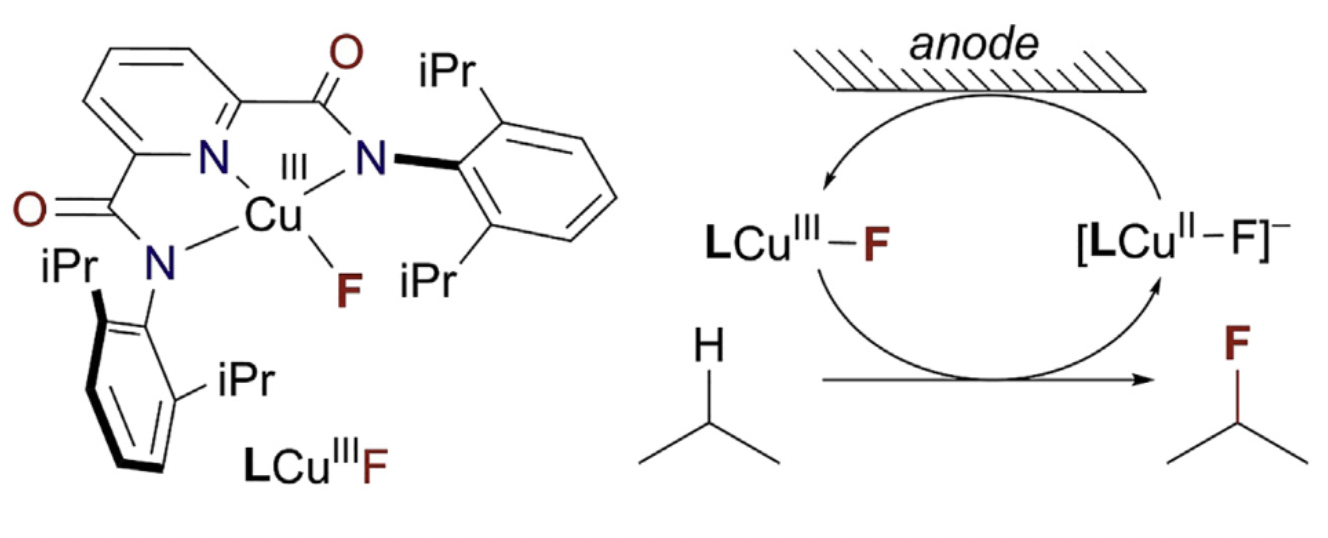
28. Copper-Catalyzed Electrochemical C–H Fluorination. Hintz, H.; Bower, J.; Tang, J.; LaLama, M.; Sevov, C.; Zhang, S. Chem Catal. 2023, 3, 100491.
27. Metal Coordination Complexes for Flow Batteries. In Flow Batteries. Silcox, B. D.; Wong, C. M.; Wei, X.; Sevov, C.; Thompson, L. T., 2023; pp 923.

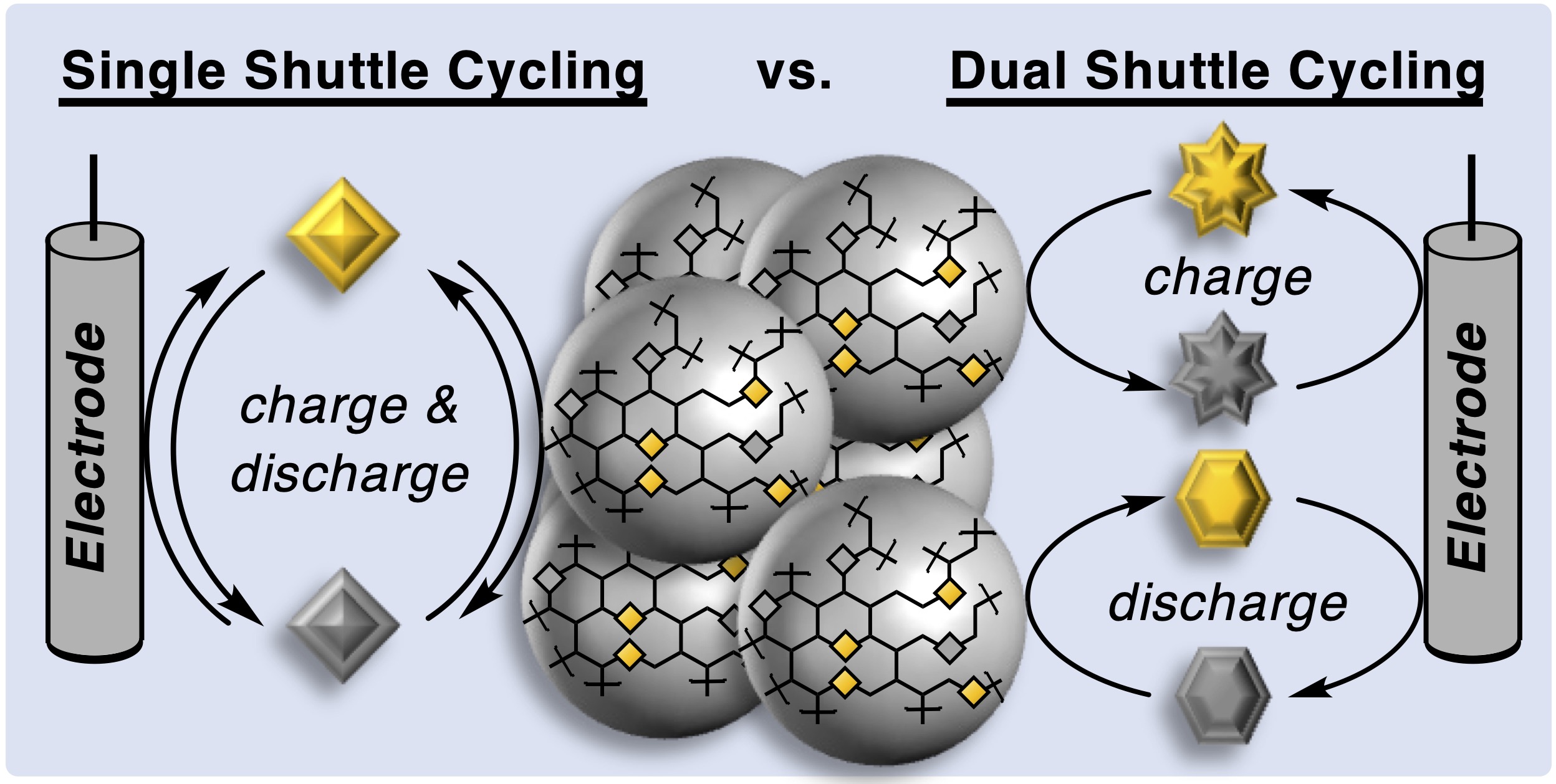
26. Single vs Dual Shuttle Cycling of Polyferrocenyl Cathodes for Redox Targeting Flow Batteries. Lee, G.; Wong, C. M.; Sevov, C. S.; ACS Energy Lett. 2022, 7, 3337.
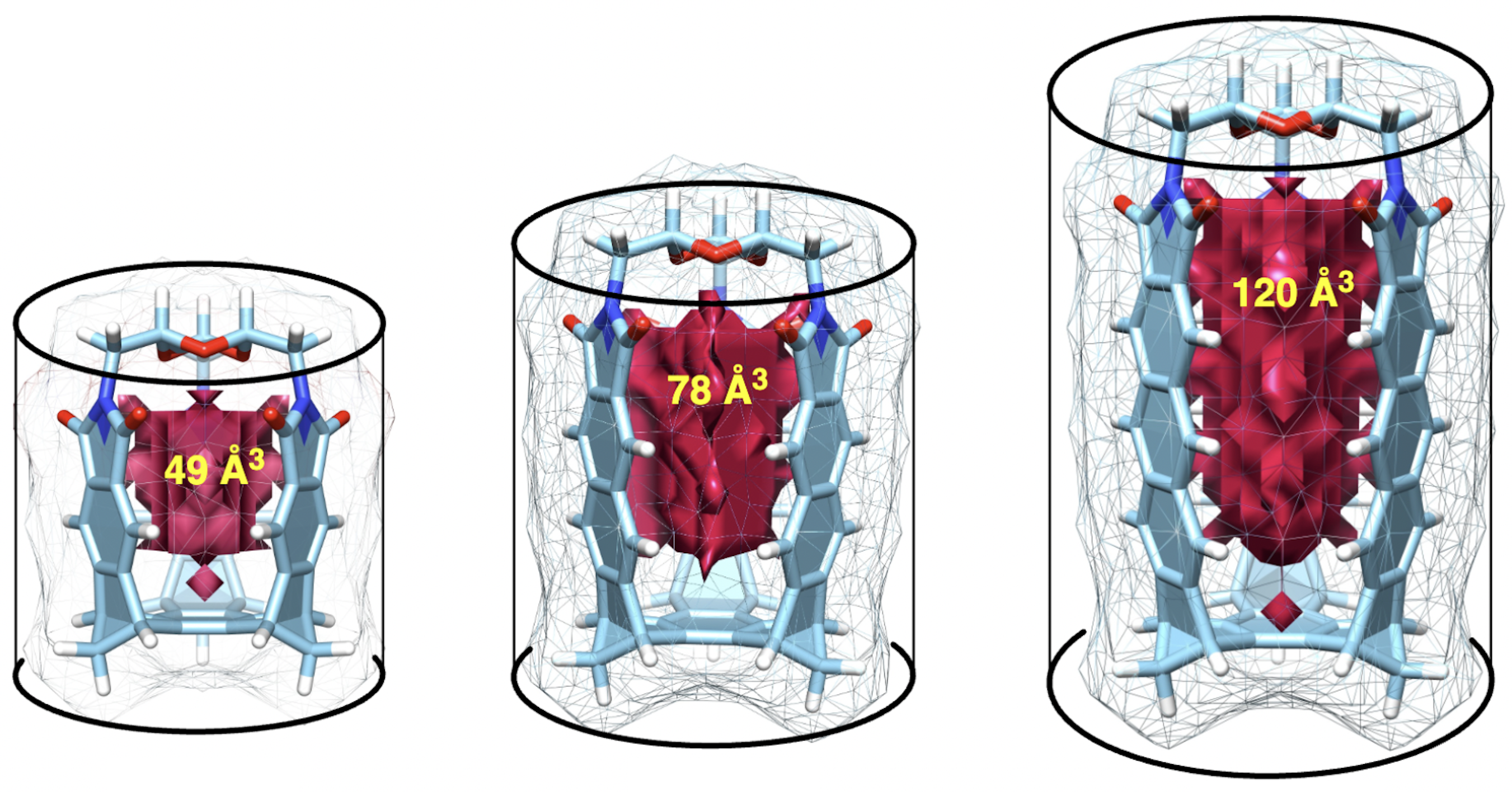
25. Closed Aromatic Tubes – Capsularenes. Pavlovic, R. Z.; Zhiquan, L.; Finnegan, T. J.; Waudby, C. A.; Wang, X.; Gunawardana V. W. L.; Zhu, X.; Wong, C. M.; Hamby, T.; Moore, C. E.; McComb, D. W.; Sevov, C. S.; Badjic, J. D. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202211304.
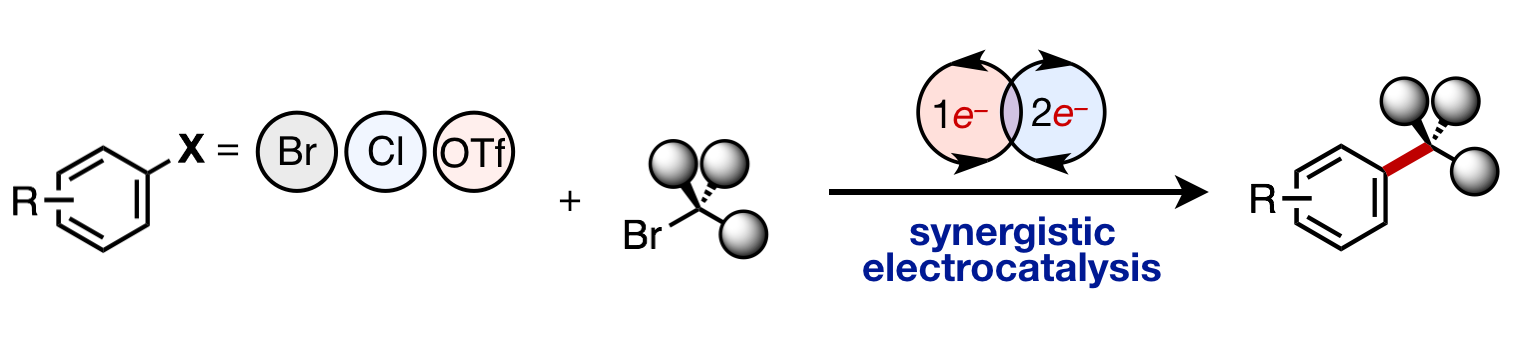
24. Controlling Ni Redox States by Dynamic Ligand Exchange for Electroreductive Csp3-Csp2 Coupling. Hamby, T. B.; LaLama, M. J.; Sevov, C. S., Science, 2022, 376, 410.
• Highlighted in The Ohio State News
23. Catalyst-Controlled Functionalization of Carboxylic Acids by Electrooxidation of Self-Assembled Carboxyl Monolayers. Hintz, H. A.; Sevov, C. S., Nature Commun. 2022, 13, 1319.
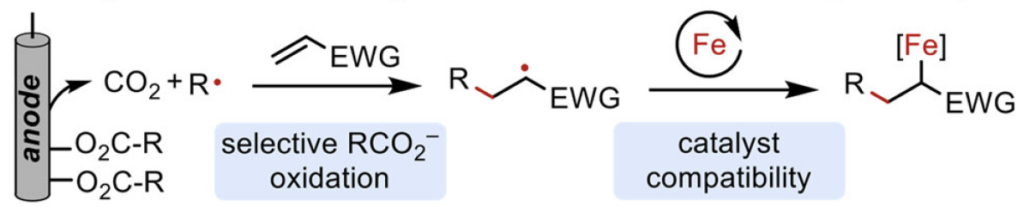
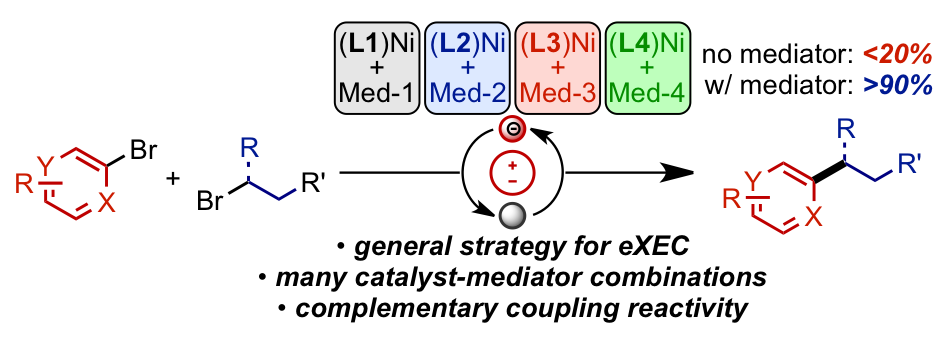
22. Synergistic Catalyst–Mediator Pairings for Electroreductive Cross-Electrophile Coupling Reactions. Zackasee, J. L. S.; Al Zubaydi, S.; Truesdell, B. L.; Sevov, C. S., ACS Catal. 2022, 12, 1161.
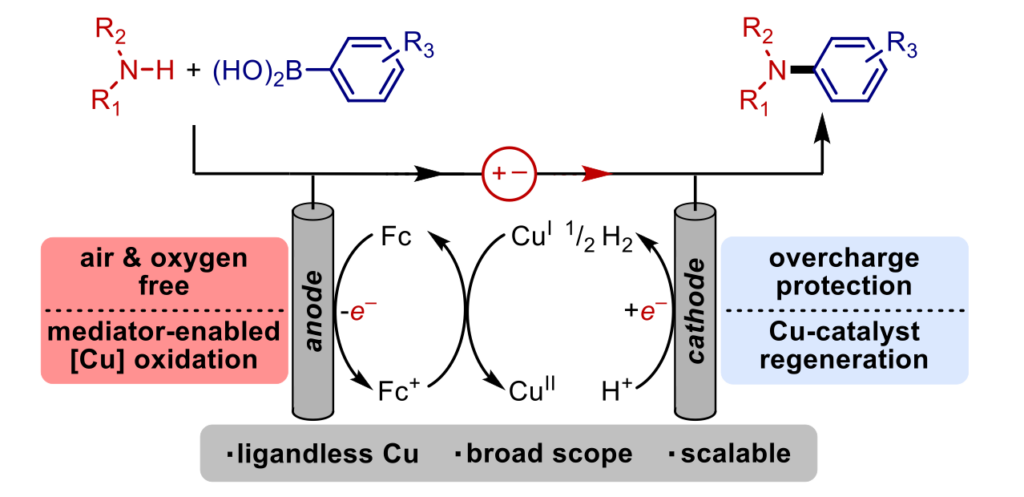
21. Mediator-Enabled Electrocatalysis with Ligandless Copper for Anaerobic Chan-Lam Coupling Reactions. Walker, B. R.; Manabe, S.; Brusoe, A. T.; Sevov, C. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 6257.
-
- Highlighted in OPR&D
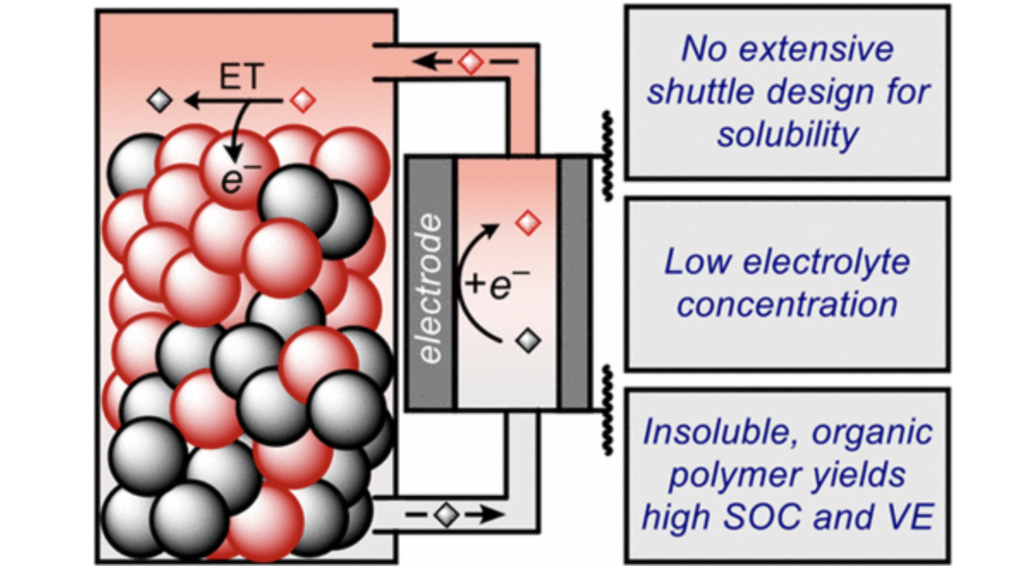
20. All-Organic Storage Solids and Redox Shuttles for Redox-Targeting Flow Batteries. Wong, C. M.; Sevov, C. S., ACS Energy Lett. 2021, 6, 1271.
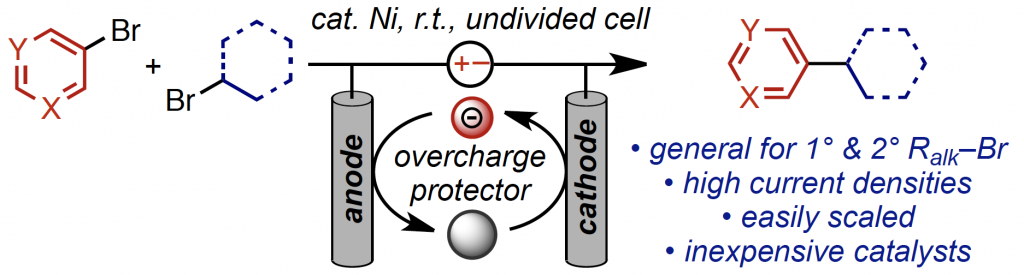
19. General C(sp2)-C(sp3) Cross-Electrophile Coupling Reactions Enabled by Overcharge Protection of Homogeneous Electrocatalysts. Truesdell, B. L.; Hamby, T. B.; Sevov, C. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 5884.
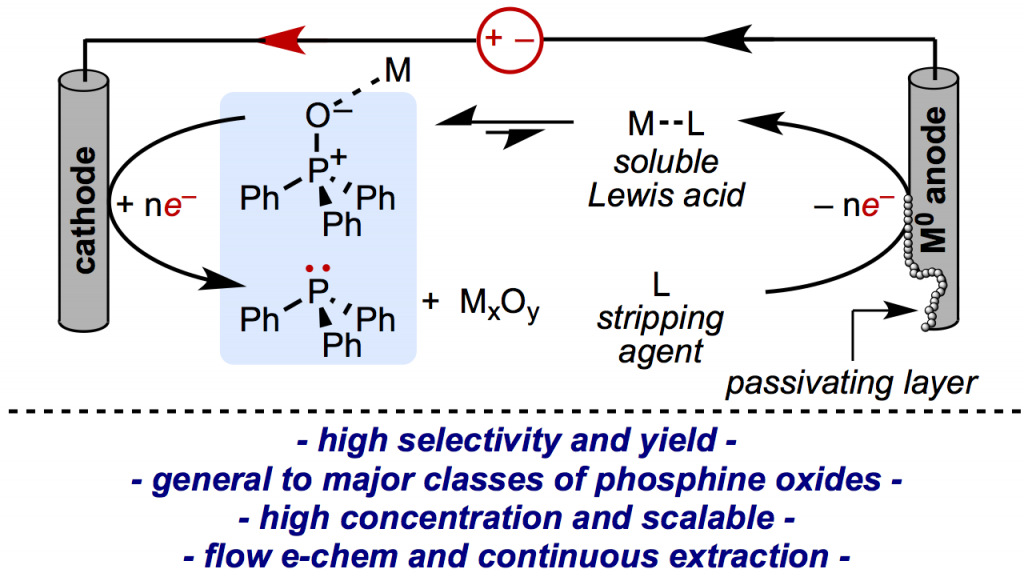
18. Direct and Scalable Electroreduction of Triphenylphosphine Oxide to Triphenylphosphine. Manabe, S.; Wong, C. M.; Sevov, C. S., J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3024.

-
- Selected as JACS Cover
- Write-up in Chemical Engineering magazine.
- Press release on Electrifying Aluminum
- Highlighted by the Sustainability Institute
17. An Electrochemically-Promoted, Nickel-Catalyzed, Mizoroki-Heck Reaction. Walker, B. R.; Sevov, C. S., ACS Catal. 2019, 9, 7197.
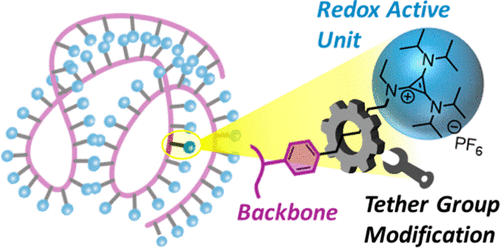
16. Effect of the Backbone Tether on the Electrochemical Properties of Soluble Cyclopropenium Redox-Active Polymers. Montoto, E. C.; Cao, Y.; Hernández-Burgos, K.; Sevov, C. S.; Braten, M. N.; Helms, B. A.; Moore, J. S.; Rodríguez-López, J., Macromolecules 2018, 10, 3539.
-
- Selected as Journal Cover
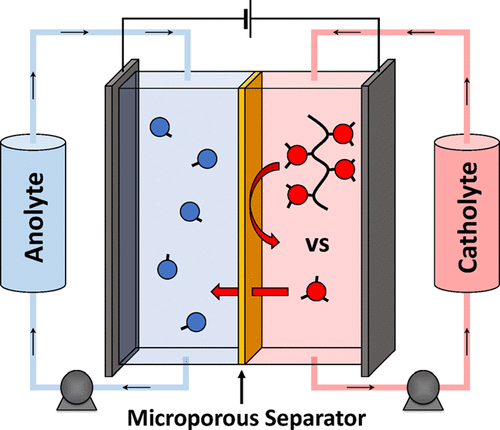
15. High-Performance Oligomeric Catholytes for Effective Macromolecular Separation in Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. Hendriks, K. H.; Robinson, S. G.; Braten, M. N.; Sevov, C. S.; Helms, B. A.; Sigman, M. S.; Minteer, S. D.; Sanford, M. S. ACS Cent. Sci. 2018, 4, 189.
-
- Link to Highlight
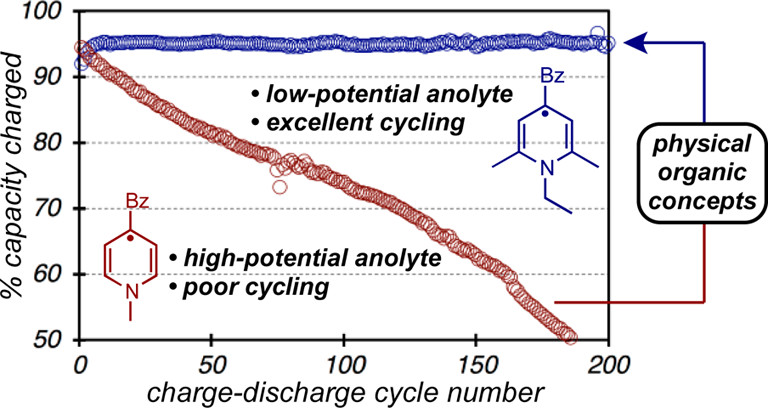
14. Low-Potential Pyridinium Anolyte for Aqueous Redox Flow Batteries. Sevov, C. S.; Hendriks, K. H.; Sanford, M. S. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 24376.
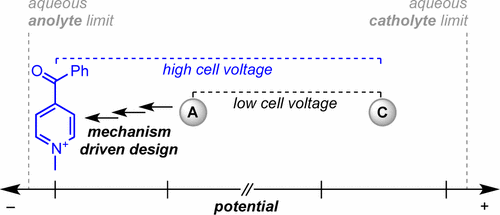
13. Multielectron Cycling of a Low-Potential Anolyte in Alkali Metal Electrolytes for Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. ‡Hendriks, K. H.; ‡Sevov, C. S.; Cook, M. E.; Sanford, M. S. ACS Energy Lett. 2017, 2, 2430. (‡Equal Contribution)
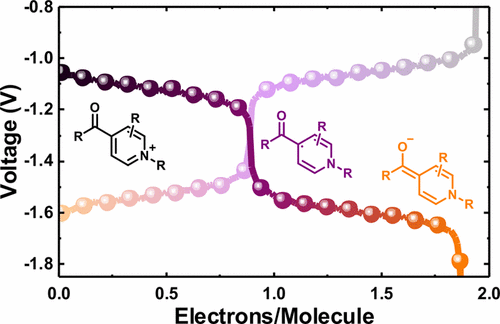
12. Physical Organic Approach to Persistent, Cyclable, Low-Potential Electrolytes for Flow Battery Applications. Sevov, C. S.; Hickey, D. P.; Cook, M. E.; Robinson, S. G.; Barnett, S.; Minteer, S. D.; Sigman, M. S.; Sanford, M. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 2924.
-
- Selected as JACS Cover
11. Macromolecular Design Strategies for Preventing Active-Material Crossover in Non-Aqueous All-Organic Redox-Flow Batteries. Doris, S. E.; Ward, A. L.; Baskin, A.; Frischmann, P. D.; Gavvalapalli, N.; Chénard, E.; Sevov, C. S.; Prendergast, D.; Moore, J. S.; Helms, B. A. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 1595.
10. Cyclopropenium Salts as Cyclable, High-Potential Catholytes in Nonaqueous Media. Sevov, C. S.; Samaroo, S. K.; Sanford, M. S. Adv. Energy Mater. 2016, 1602027. 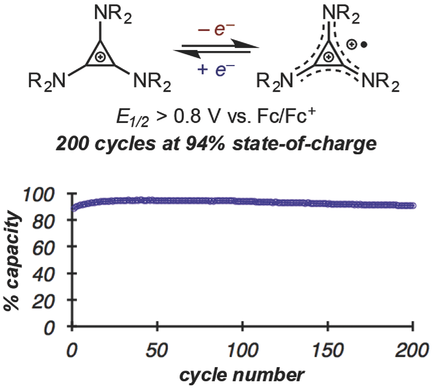
9. Mechanism-Based Development of a Low-Potential, Soluble, and Cyclable Multielectron Anolyte for Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. ‡Sevov, C. S.; ‡Fisher, S. L.; Thompson, L. T.; Sanford, M. S. J Am Chem Soc 2016, 138, 15378. (‡Equal Contribution)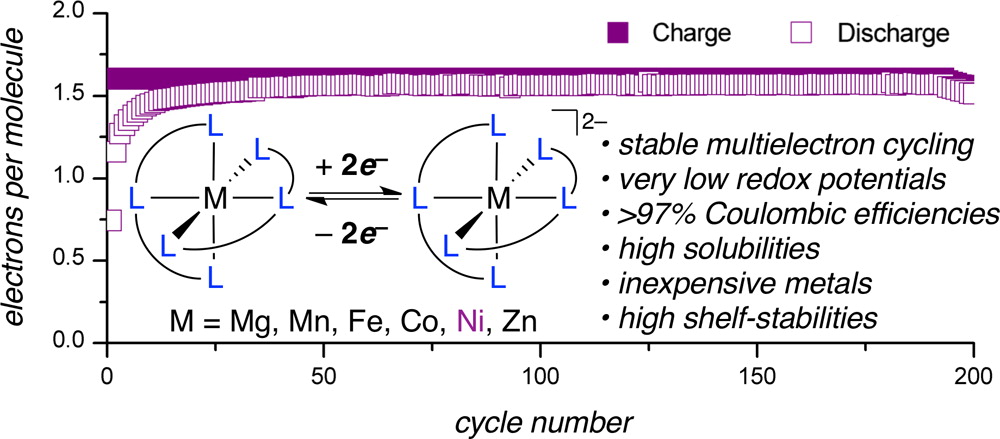
8. Evolutionary Design of Low Molecular Weight Organic Anolyte Materials for Applications in Nonaqueous Redox Flow Batteries. Sevov, C. S.; Brooner, R. E. M.; Chénard, E.; Assary, R. S.; Moore, J. S.; Rodríguez-López, J.; Sanford, M. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14465. 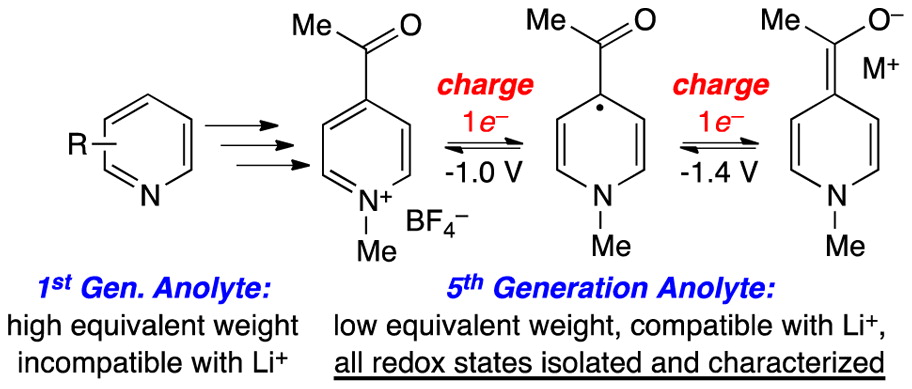
7. Iridium-Catalyzed Oxidative Olefination of Furans with Unactivated Alkenes. Sevov, C. S.; Hartwig, J. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 10625.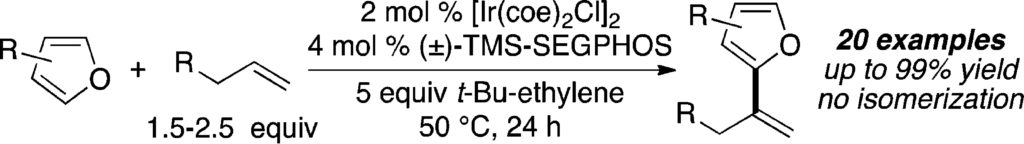
6. Iridium-Catalyzed, Intermolecular Hydroamination of Unactivated Alkenes with Indoles. Sevov, C. S.; Zhou, J.; Hartwig, J. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3200.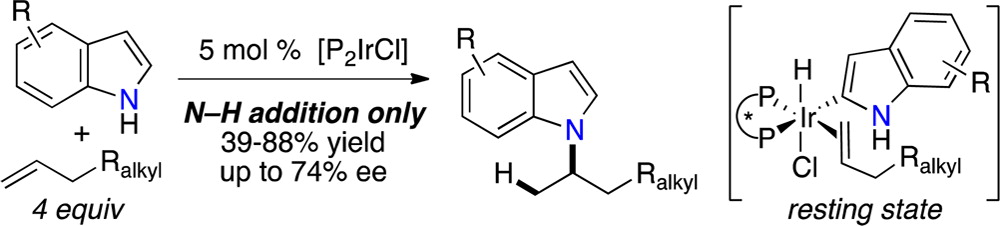
5. Iridium-Catalyzed, Intermolecular Hydroetherification of Unactivated Aliphatic Alkenes with Phenols. Sevov, C. S.; Hartwig, J. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9303.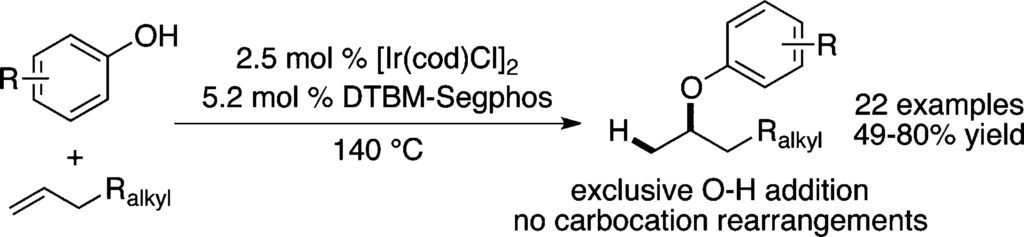
4. Iridium-Catalyzed Intermolecular Asymmetric Hydroheteroarylation of Bicycloalkenes. Sevov, C. S.; Hartwig, J. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 2116. 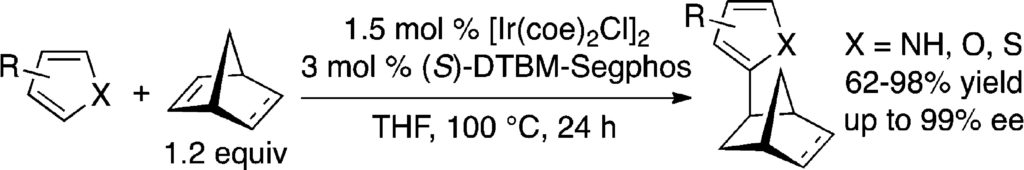
3. Iridium-Catalyzed Intermolecular Hydroamination of Unactivated Aliphatic Alkenes with Amides and Sulfonamides. Sevov, C. S.; Zhou, J.; Hartwig, J. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 11960.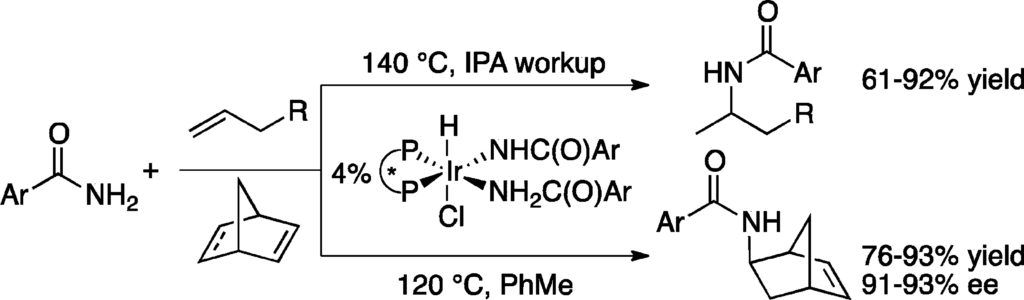
2. Selectivity in Radical Cation Cycloadditions. Sevov, C. S.; Wiest, O. In Carbon-Centered Free Radicals and Radical Cations: Structure, Reactivity, and Dynamics; Forbes, M. D. E., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, 2010; Vol. 1, p 61; ISBN: 978-0-470-39009-2
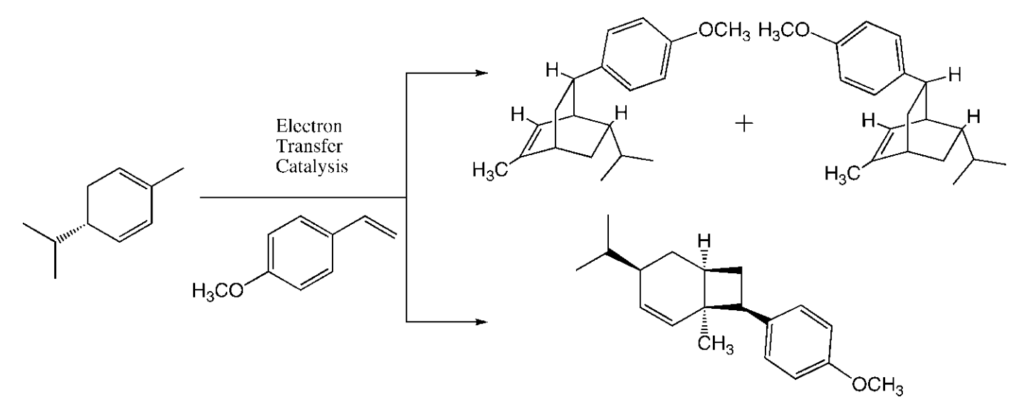
1. Selectivity in the Electron Transfer Catalyzed Diels-Alder Reaction of (R)-Alpha-Phellandrene and 4-Methoxystyrene. Sevov, C. S.; Wiest, O. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 73, 7909.